TYPES OF VECTOR
1.) Equal Vectors : Two vectors of equal magnitude, in same direction are called equal vectors.

2.) Negative Vectors : Two vectors of equal magnitude but in opposite directions are called negative vectors.

3.) Zero Vector or Null Vector : A vector whose magnitude is zero is known as a zero or null vector. Its direction is not defined. It is denoted by 0.
Velocity of a stationary object, acceleration of an object moving with uniform velocity and resultant of two equal and opposite vectors are the examples of null vector.
4.) Unit Vector : A vector having unit magnitude is called a unit vector.
A unit vector in the direction of vector A is given by
 = A / A
A unit vector is unitless and dimensionless vector and represents direction only.
5.) Orthogonal Unit Vectors : The unit vectors along the direction of orthogonal axis, i.e., X – axis, Y – axis and Z – axis are called orthogonal unit vectors. They are represented by

6.) Co-initial Vectors : Vectors having a common initial point, are called co-initial vectors.
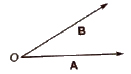
7.) Collinear Vectors : Vectors having equal or unequal magnitudes but acting along the same or Ab parallel lines are called collinear vectors.
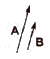
8.) Coplanar Vectors : Vectors acting in the same plane are called coplanar vectors.
9.) Localised Vector : A vector whose initial point is fixed, is called a localised vector.
10.) Non-localised or Free Vector : A vector whose initial point is not fixed is called a non-localised or a free vector.
11.) Position Vector : A vector representing the straight line distance and the direction of any point or object with respect to the origin, is called position vector.

Comments
Post a Comment