ADDITION OF VECTORS
#. Addition of Vectors :-
1. Triangle Law of Vectors
If two vectors acting at a point are represented in magnitude and direction by the two sides of a triangle taken in one order, then their resultant is represented by the third side of the triangle taken in the opposite order.
If two vectors A and B acting at a point are inclined at an angle θ, then their resultant
R = √A2 + B2 + 2AB cos θ
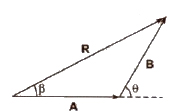
If the resultant vector R subtends an angle β with vector A, then
tan β = B sin θ / A + B cos θ.
2. Parallelogram Law of Vectors
If two vectors acting at a point are represented in magnitude and direction by the two adjacent sides of a parallelogram draw from a point, then their resultant is represented in magnitude and direction by the diagonal of the parallelogram draw from the same point.

Resultant of vectors A and B is given by
√A2 + B2 + 2AB cos θ
If the resultant vector R subtends an angle β with vector A, then
tan β = B sin θ / A + B cos θ.
3. Polygon Law of Vectors
It states that if number of vectors acting on a particle at a time are represented in magnitude and direction by the various sides of an open polygon taken in same order, their resultant vector E is represented in magnitude and direction by the closing side of polygon taken in opposite order. In fact, polygon law of vectors is the outcome of triangle law of vectors.
R = A + B + C + D + E
OE = OA + AB + BC + CD + DE

#. Properties of Vector Addition
(i) Vector addition is commutative, i.e., A + B = B + A
(ii) Vector addition is associative, i.e.,
A +(B + C)= B + (C + A)= C + (A + B)
(iii) Vector addition is distributive, i.e., m (A + B) = m A + m B.

Comments
Post a Comment